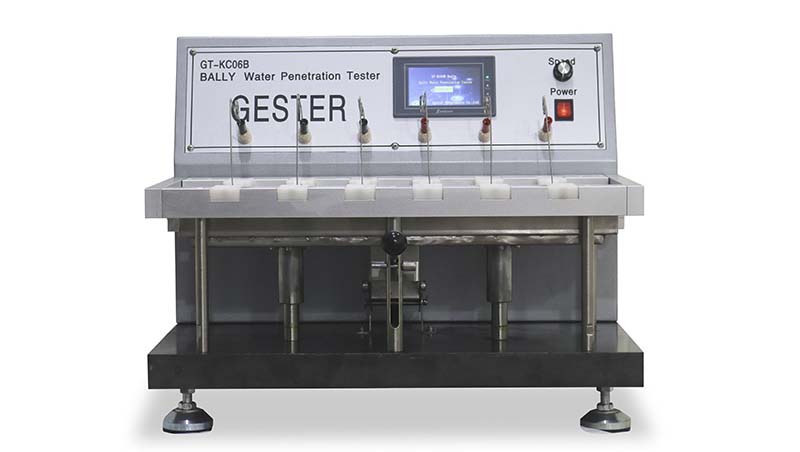

The BALLY Water Penetration Tester Of Leather is primarily used to evaluate the resistance of footwear upper materials—such as leather, synthetic leather, and various fabrics—to water penetration under flexing conditions. The testing process involves simulating the conditions that materials may face during regular wear, especially in environments where exposure to water is a concern. By assessing the water permeability of these materials, manufacturers can determine their suitability for use in different applications, ensuring that the final products meet durability and quality standards.
To guarantee that the results of the testing are reliable and meet global requirements, the BALLY Water Penetration Tester Of Leather is designed to comply with a number of international standards. These standards ensure that the device provides consistent and reproducible results. Some of the key standards include:
The Working Principle of the Bally water penetrometer
Understanding the principle behind the operation of the Bally water penetrometer is crucial for interpreting its results accurately. Here’s how it works:
Sample Preparation:
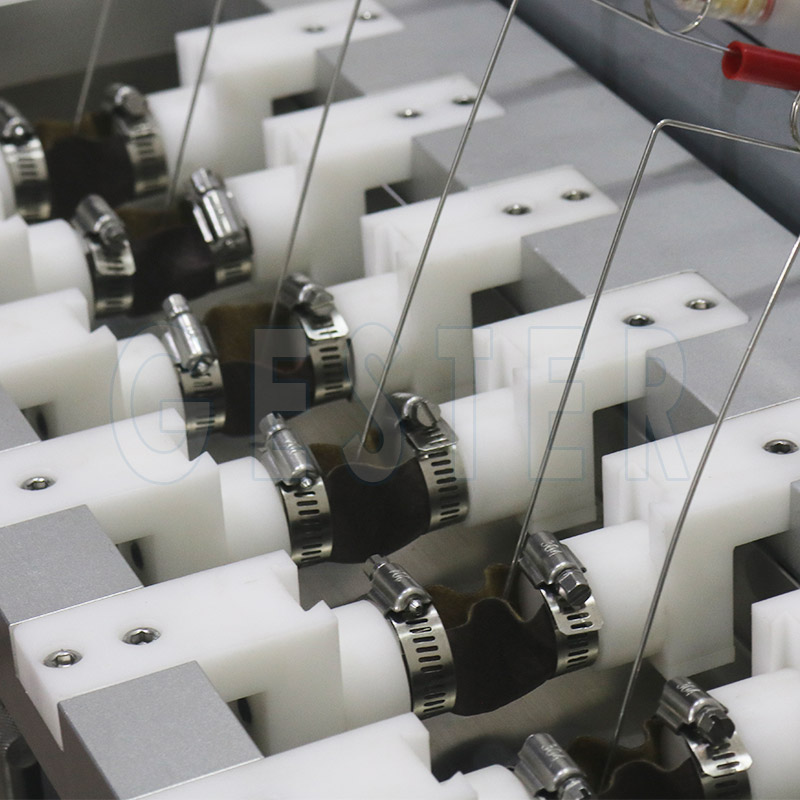
A rectangular test specimen—typically the material to be tested, such as leather, fabric, or artificial leather—is selected.
Mounting the Specimen:
The specimen is then bent around two cylindrical clamps, forming a trough. These clamps securely hold the material in place, ensuring that it remains stationary during testing. The flexibility of the material is crucial, as the test is designed to assess how the material performs under repeated bending or flexing.
Immersion in Water:
The trough, which now holds the sample, is immersed in water.
Flexing Action:
The clamps oscillate at a constant speed, causing the specimen to flex repeatedly. This motion is crucial because it simulates the bending and flexing that materials undergo when worn, particularly in shoes or other wearable products.
Measuring Water Penetration:
The primary goal of the test is to measure the time it takes for water to penetrate the material. As the specimen is flexed, the water will eventually seep through, and this time is recorded. Additionally, the mass of water absorbed by the specimen and transmitted through the material can also be measured.
The results of the test indicate the resistance of the material to water penetration. A longer time for water penetration and a lower mass of absorbed water are indicative of better water resistance, making the material more suitable for use in environments where exposure to water is a concern.
Best Practices for Using the BALLY Water Penetration Tester
To achieve accurate and reliable results when using the BALLY Water Penetration Tester, manufacturers should follow best practices to ensure the integrity of the test process. Below are some essential tips:
Ensure Correct Specimen Preparation:
The material being tested must be prepared according to the standards. This includes cutting the material to the proper dimensions and ensuring that it is clean and free from any contaminants that may affect the test results.
Calibrate the Tester Regularly:
To maintain the accuracy of test results, the BALLY Water Penetration Tester should be calibrated periodically. This includes checking the mechanical components.
Control Environmental Factors:
Environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, can affect the water resistance of materials. It’s important to conduct tests in a controlled environment to eliminate variables that could influence the outcome.
Replicate Tests for Consistency:
For more reliable results, it’s often a good practice to run multiple tests on the same material and average the outcomes. This reduces the potential for error and provides a more accurate representation of the material’s performance.
Monitor for Wear and Tear on the Tester:
Over time, the bally penetrometer water penetration tester may experience wear from frequent use. Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to keep the device in optimal working condition.